Turmeric is able to destroy cancer cells.: IIT Chennai
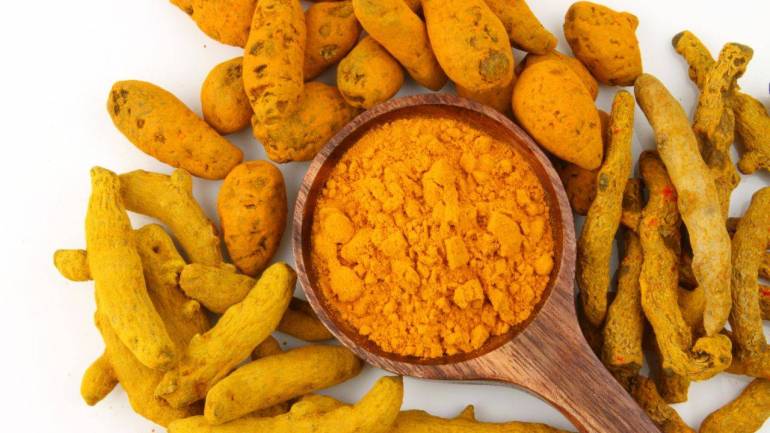

Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology, Chennai (IIT Chennai), in their recent research, found that turmeric and the curcumin (curcumin) found in it are known to be the most active ingredients in turmeric. Benefits of turmeric Most of the antibodies present in it come from curcumin) (active principle) are capable of destroying cancer cells.
The study also showed that curcumin further activated the sensitivity of leukaemia cells to the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). Has increased. TRAIL is, in fact, a protein that acts to kill cancer cells. School of Biosciences, Department of Biotechnology, IIT Madras Head of Research Prof. Rama Shankar Verma, Bhupat and Jyoti Mehta have done this research.
These researches have recently been published in the well-known peer-review journal Pharmacological Reports. Researchers report that the results of the research have been tested in-situ (in a test tube). Therefore, it cannot be said with certainty that the results will be as effective on the human body as in clinical trials. Actually the blood in our intestine is weak in absorbing the curcumin present in turmeric, so there are doubts about the efficacy of the research.
Onion, green pepper are also helpful
This research by researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, showed that turmeric and curcumin showed new light to eliminate cancer cells. The study showed that in addition to curcumin, some researchers have shown that elements such as quercetin found in onions and green tea and piperigen found in black and green peppers also increase the absorption of curcumin.
Research is important
Scientists have considered curcumin to be an anti-cancer agent due to its ability to be anti-cancerous and to activate apoptosis in various cancer cells. At the same time, apoptosis is known to eliminate cancer cells and that is why it is traditionally used to kill cancer cells.
Researchers used isotype control of related and diverse patient groups for analysis. They investigated the ability of curcumin to modify the TRAIL pathway in leukemic cells.